
As an Estimator using Trimble Business Center for fast accurate Takeoffs, we provide a range of tools to increase your productivity and ease of creating the final deliverables.
Our resource libraries provide you with Custom Menus, Toolbars and Shortcuts to improve your workflows, Project and Drafting Templates to get you started and provide drawing creation automation for Plans, Profiles, Sections and Custom Sheet Layouts in addition to providing you with Materials Libraries and a structured workflow to get the job done.
Our Training and Support program will train your users how to use TBC and how to execute the Takeoff workflows, accelerate your learning and user development to get results quicker and with increased accuracy.
Create and manage boundaries, boundary collections and boundary groups. Compute and store volume calculations for later recall. Label and annotate drawings with volume labels and tables and generate volume reports for a variety of volumetric scenarios e.g. Stockpiles, Progress, Cut / Fill, Pay Quantities etc.
Reports the plan and slope areas for cut and fill broken down by specified slope ranges on each of two surfaces. The report uses the isopach computed between the two surfaces (e.g. Existing and Subgrade Adjusted Finished Grade) to determine cut and fill areas and then sums the areas of triangles of both surfaces that fall within the defined slope ranges within the computed cut and fill areas. Ideal for the determination of surface finishing / trim areas in fill scenarios.
Utilizes the RPS New Layer control to create a new layer, new layer group and assign layer properties including the takeoff categorization, potential site improvement or surface boundaries and associated site improvement attributes.

The RPS Relayer command provides increased productivity when relayering CAD objects to a number of different layers. The user can establish any number of target layers and then simply select the objects to relayer, tag the layer that they want to move them to and OK to execute. The fact that you can relayer to multiple layers quickly and easily can take significant time out of data prep processes.

Utilizes the RPS New Layer control to create a new layer, new layer group and assign layer properties including the takeoff categorization, potential site improvement or surface boundaries and associated site improvement attributes.

The RPS Relayer command provides increased productivity when relayering CAD objects to a number of different layers. The user can establish any number of target layers and then simply select the objects to relayer, tag the layer that they want to move them to and OK to execute. The fact that you can relayer to multiple layers quickly and easily can take significant time out of data prep processes.
Create multiple copies of any objects quickly on the same or different layers, in 2D or 3D and in any view
Provides manual and fully automated methods to join CAD or PDF vector lines together quickly and easily. Solves common problems like line gaps, overlaps, crossovers, lateral gaps, lines on different layers, lines with different names or colors to provide an extremely fast way to join lines. Line segments can be selected in the most convenient location not just at the ends that you wish to join.
Provides the ability to crop selected lines either side of a selected line or to remove the segments of selected lines between a pair of lines. This is useful to remove e.g. Contour lines from pavement areas or around curb and gutter sections, where more precise modeling techniques are being used.
Name by Layer - Names line objects using the name of the objects layer. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.
Layer by Name - Relayers objects based on the objects name. Layered objects can be placed in Layer Groups using a Layer Group mapping using filter elements of the objects name. This is useful for organizing surveyed data e.g. for utility relocates
Reverse the direction of selected linestrings, CAD lines or polylines using a simple switch direction, align to an alignment or reference line, clockwise / anticlockwise (closed lines), or align with slope (from first to last node of the selected lines).
Creates 2D and 3D linestrings with a range of controls to manage elevation input and formulaic adjustment including 2D, single height, multiheight, multiheight auto and multiheight from surface. Also includes ability to create lines with a preset number of nodes, can autoclose and provide grip editing while in the command. Can also create curve elements and VPI only nodes also. Ideal for takeoff digitizing of linework or for data prep purposes.
Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.

Provides manual and fully automated methods to join CAD or PDF vector lines together quickly and easily. Solves common problems like line gaps, overlaps, crossovers, lateral gaps, lines on different layers, lines with different names or colors to provide an extremely fast way to join lines. Line segments can be selected in the most convenient location not just at the ends that you wish to join.

Provides the ability to crop selected lines either side of a selected line or to remove the segments of selected lines between a pair of lines. This is useful to remove e.g. Contour lines from pavement areas or around curb and gutter sections, where more precise modeling techniques are being used.

Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.
Provides a work process tool to cleanup and sort imported CAD files. The command includes a CAD Block processor to manage and explode imported blocks, a Layer control to manage and group imported layers based on predefined rulesets, and a set of miscellaneous controls to delete imported plan sets, delete AEC object references, zero length lines and empty unprotected layers, change text to multiline text and change text styles to stroke fonts for improved graphics speed.
Imported Solids, 3DShell or mesh objects from IFC, DWG and DGN files can be exploded into component lines and points using this command. The command handles solids by breaking them into top, bottom and side objects or 3D polygons on separate layers so that the data can be used as source data for surface models. 3D linear features can be re-created through use of the Filter by Alignment command.

Provides a rapid way to mass convert polyline and CAD line objects into linestring objects. In addition the command provides an easy way to eliminate UCS (User Defined Coordinate Systems) from imported CAD objects or from objects created using the Cutting Plane View in TBC. You can also use this tool to eliminate horizontal or vertical vertices from selected linestrings e.g. to reduce nodes in contours or VPIs from imported CAD 3D lines. This increases your productivity and eliminates a large bottleneck in the processing of CAD data and point clouds.

Imported Solids, 3DShell or mesh objects from IFC, DWG and DGN files can be exploded into component lines and points using this command. The command handles solids by breaking them into top, bottom and side objects or 3D polygons on separate layers so that the data can be used as source data for surface models. 3D linear features can be re-created through use of the Filter by Alignment command.

Name by Layer - Names line objects using the name of the objects layer. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.
Layer by Name - Relayers objects based on the objects name. Layered objects can be placed in Layer Groups using a Layer Group mapping using filter elements of the objects name. This is useful for organizing surveyed data e.g. for utility relocates

Reverse the direction of selected linestrings, CAD lines or polylines using a simple switch direction, align to an alignment or reference line, clockwise / anticlockwise (closed lines), or align with slope (from first to last node of the selected lines).

Provides a rapid way to mass convert polyline and CAD line objects into linestring objects. In addition the command provides an easy way to eliminate UCS (User Defined Coordinate Systems) from imported CAD objects or from objects created using the Cutting Plane View in TBC. You can also use this tool to eliminate horizontal or vertical vertices from selected linestrings e.g. to reduce nodes in contours or VPIs from imported CAD 3D lines. This increases your productivity and eliminates a large bottleneck in the processing of CAD data and point clouds.
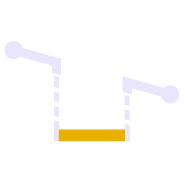
Provides a quick and easy way to null out or modify VPIs on selected sections of 3D linestrings, adjust and prorate elevations for bridge beam deflections or to taper linework over selected distances to match existing grade. You can use this command in Spot mode to elevate lines. Plane Mode allows you to elevate e.g. curb lines onto tilted planes defined by 3 points. Surface Mode allows you to elevate e.g. curb lines onto a grading framework surface e.g. for Parking Lots. In Plane and Surface Mode you can specifically define how points are created around curve sections to improve the quality and consistency of your models.
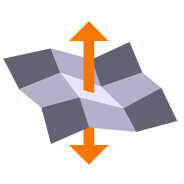
Computes a surcharge / overexcavation surface by adding a % of cut or fill depth to a selected surface. Can also be used to adjust a surface model to match grade at project limits or at other locations e.g. at bridge decks / abutments etc

Combines multiple TIN surfaces from a design into a single TIN surface model comprising multiple islands. For example where an over excavation surface on a corridor model comes and goes along the alignment, or where the left embankment and right embankment were designed as separate components and you want to combine them into a single surface for TBC corridor or machine control purposes.
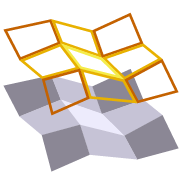
Explodes a selected TIN surface model into 3D lines and or points. The explode process eliminates duplicate lines. The exploded surface can then be edited to remove erroneous data e.g. erroneous triangle sides or to be combined with other data to create a new surface model. Explode process also provides advanced filter controls to facilitate breakline, drapeline and boundary identification and extraction.
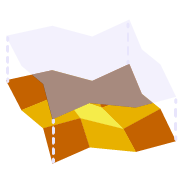
Provides the ability to offset an entire surface or an area of a surface within a clipping boundary to create a new surface model. This is a quick and easy tool to create e.g. Topsoil Strip surfaces from an Existing Ground surface model.

Computes a surcharge / overexcavation surface by adding a % of cut or fill depth to a selected surface. Can also be used to adjust a surface model to match grade at project limits or at other locations e.g. at bridge decks / abutments etc

Combines multiple TIN surfaces from a design into a single TIN surface model comprising multiple islands. For example where an over excavation surface on a corridor model comes and goes along the alignment, or where the left embankment and right embankment were designed as separate components and you want to combine them into a single surface for TBC corridor or machine control purposes.

Explodes a selected TIN surface model into 3D lines and or points. The explode process eliminates duplicate lines. The exploded surface can then be edited to remove erroneous data e.g. erroneous triangle sides or to be combined with other data to create a new surface model. Explode process also provides advanced filter controls to facilitate breakline, drapeline and boundary identification and extraction.
Template driven command that creates multiple offset lines (fully curvilinear lines) for multiple surfaces (finished grade and subgrade) on multiple layers (one per feature line) from selected source lines defined using offset and elevation, offset and delta elevation, offset and slope definitions. Ideal for curb & gutter, barriers, gabion walls, site /subdivision roads and more.
Create a new 3D line at an offset and elevation difference to a selected pair of lines where the elevation of the new line is computed by extending the slope defined by the selected pair of lines and applying the elevation difference required. This tool is great for extending pavement or subgrade surfaces where the pavement surface is defined by imported 3D string (lines) data.

Provides the ability to offset an entire surface or an area of a surface within a clipping boundary to create a new surface model. This is a quick and easy tool to create e.g. Topsoil Strip surfaces from an Existing Ground surface model.
Provides the ability to create points and or lines using station and combination of either Offset and Elevation, Offset and Delta Elevation, Offset and Slope, Slope and Elevation, Slope and Delta Elevation or Slope and Target Surface. This provides an effective means of defining sideslopes, benches, berms, ponds or pad areas etc.
This command provides the ability to compute 3D lines at the intersection of two slopes defined by two pairs of lines, with or without vertical or perpendicular offsets. The command is ideal for the computations of subgrade and topsoil adjusted embankment surfaces. All necessary offset lines are computed to facilitate rapid creation of the adjusted surface model.

Template driven command that creates multiple offset lines (fully curvilinear lines) for multiple surfaces (finished grade and subgrade) on multiple layers (one per feature line) from selected source lines defined using offset and elevation, offset and delta elevation, offset and slope definitions. Ideal for curb & gutter, barriers, gabion walls, site /subdivision roads and more.

Create a new 3D line at an offset and elevation difference to a selected pair of lines where the elevation of the new line is computed by extending the slope defined by the selected pair of lines and applying the elevation difference required. This tool is great for extending pavement or subgrade surfaces where the pavement surface is defined by imported 3D string (lines) data.

Provides the ability to create points and or lines using station and combination of either Offset and Elevation, Offset and Delta Elevation, Offset and Slope, Slope and Elevation, Slope and Delta Elevation or Slope and Target Surface. This provides an effective means of defining sideslopes, benches, berms, ponds or pad areas etc.
This powerful tool provides geometric selection properties for imported CAD or PDF linework. Initially conceived for the cross section takeoff workflows, this tool provides geometric controls that can be combined for extremely rapid selection and relayering of objects using length, aspect ratio and node count.
This command creates text that automatically increments between each text placement e.g. for labeling pads, parking bays or for adding station labels to PDF cross sections that have no text to use for section conversion.
This command provides two main abilities, Nudge Line and Nudge Node. Nudge Line moves a selected line laterally by a defined amount in order to fix a surface model where two lines that define the top and bottom of a vertical wall or face lie on top of each other but separated vertically. Nudge Node is for cross sections where two or more nodes in the cross section lie in the same XY location but are separated vertically.
Converts chorded linework into optimized curvilinear linestrings in both horizontal and vertical components for use in stringless paving and to improve 3D models for corridors. Can also be used to convert chorded PDF Vector lines into curvilinear lines for modeling purposes.
This command allows you to pick an alignment and a selection of linework e.g. for road pavement section lines in order to create the edge lines (pavement edge lines) in the direction of increasing station and / or a boundary around the selected lines. Part of the CAD / PDF cross sections takeoff workflow, this facilitates rapid 3D modeling from converted PDF or CAD cross sections.

Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.

Imports boring log data from a CSV file to create site (Takeoff) boring logs in order to rapidly build strata layers for earthworks quantity purposes.

Extracts vectors from georeferenced PDF images on demand using automatic and manual process controls. Lines can be layered, joined and elevated in the process, eliminating multiple Takeoff steps and increasing productivity.
This command creates a legend of site improvements applied to surfaces within the project either for takeoff or data modeling purposes. The legend shows the color of the site improvement and the material layer stack and defined material thicknesses for each site improvement used. This automates the creation of drawings for submittals or for use by site personnel to understand a project.

Creates 2D and 3D linestrings with a range of controls to manage elevation input and formulaic adjustment including 2D, single height, multiheight, multiheight auto and multiheight from surface. Also includes ability to create lines with a preset number of nodes, can autoclose and provide grip editing while in the command. Can also create curve elements and VPI only nodes also. Ideal for takeoff digitizing of linework or for data prep purposes.

Provides a fast and easy way to determine the surface and plan areas of bounded areas on surface models. The surface areas can be defined by collections of 3D breaklines in the surface with the "Sharp and Texture" property, or areas of the surface where surface textures have been defined. The computed areas can be labeled on the drawing using this command.

This powerful tool provides geometric selection properties for imported CAD or PDF linework. Initially conceived for the cross section takeoff workflows, this tool provides geometric controls that can be combined for extremely rapid selection and relayering of objects using length, aspect ratio and node count.
This command creates text that automatically increments between each text placement e.g. for labeling pads, parking bays or for adding station labels to PDF cross sections that have no text to use for section conversion.

This command provides two main abilities, Nudge Line and Nudge Node. Nudge Line moves a selected line laterally by a defined amount in order to fix a surface model where two lines that define the top and bottom of a vertical wall or face lie on top of each other but separated vertically. Nudge Node is for cross sections where two or more nodes in the cross section lie in the same XY location but are separated vertically.

This command allows you to pick an alignment and a selection of linework e.g. for road pavement section lines in order to create the edge lines (pavement edge lines) in the direction of increasing station and / or a boundary around the selected lines. Part of the CAD / PDF cross sections takeoff workflow, this facilitates rapid 3D modeling from converted PDF or CAD cross sections.

Converts chorded linework into optimized curvilinear linestrings in both horizontal and vertical components for use in stringless paving and to improve 3D models for corridors. Can also be used to convert chorded PDF Vector lines into curvilinear lines for modeling purposes.

Copy data from one project to another or within an existing project using our virtual VCL file via the Windows clipboard. Ideal for creating copies of sheet sets complete with all settings within a project or for transferring information from one project into another without having to use Export and Import processes.
Paste information from the Windows clipboard directly into your project drawings. Use with your favorite Windows clipping tool (Snagit, Snip and Paste etc.) to capture PDF sheet details, excel spreadsheet tables, images, text or virtual VCL data generated using RPS Copy to Clipboard command.
Point clouds can be used to create surface models. The resulting surfaces can be large and are hard to report for QA / QC purposes. This command converts a TIN surface, optionally clipped to a boundary into a grid of points based on a regular or alignment based grid, and computes cut / fill values to a reference surface with applied high and low tolerances for reporting purposes.

Provides the ability to use voice input to execute any TBC command. This improves productivity and allows the commands to execute as well as the command dialog to be navigated without mouse movement.

Copies a layer group and all the layers (that have members) into a new layer group where the group and each layer is named using the existing name with an added prefix or suffix.

Copies a layer group and all the layers (that have members) into a new layer group where the group and each layer is named using the existing name with an added prefix or suffix.
A simple editing tool to add additional segments into an existing linestring. Simply click where you require additional nodes and the linestring selected updates by adding additional segments into the existing linestring. You can use this command to insert segments into the line or to add segments at either end of the line.
Create 3D linestrings quickly without the complexity of the Linestring Editor.

Switch text properties between two selected text objects. Text properties include height, width, text, rotation, oblique angle, justification, aspect ratio, layer, color etc.

Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.

A simple editing tool to add additional segments into an existing linestring. Simply click where you require additional nodes and the linestring selected updates by adding additional segments into the existing linestring. You can use this command to insert segments into the line or to add segments at either end of the line.

Create 3D linestrings quickly without the complexity of the Linestring Editor.

Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.

Provides a rapid way to mass convert polyline and CAD line objects into linestring objects. In addition the command provides an easy way to eliminate UCS (User Defined Coordinate Systems) from imported CAD objects or from objects created using the Cutting Plane View in TBC. You can also use this tool to eliminate horizontal or vertical vertices from selected linestrings e.g. to reduce nodes in contours or VPIs from imported CAD 3D lines. This increases your productivity and eliminates a large bottleneck in the processing of CAD data and point clouds.

Provides the ability to filter a selection of objects in relation to a selected reference line or alignment. User can define parallel or perpendicular or up to a specified skew angle to rapidly find linear features or cross section lines across surfaces. Useful tool with Explode Surface or Explode IFC Shell commands.
Converts selected linework into AOIs for Takeoff reports (Areas of Interest).

Provides a rapid way to mass convert polyline and CAD line objects into linestring objects. In addition the command provides an easy way to eliminate UCS (User Defined Coordinate Systems) from imported CAD objects or from objects created using the Cutting Plane View in TBC. You can also use this tool to eliminate horizontal or vertical vertices from selected linestrings e.g. to reduce nodes in contours or VPIs from imported CAD 3D lines. This increases your productivity and eliminates a large bottleneck in the processing of CAD data and point clouds.

Computes a surcharge / overexcavation surface by adding a % of cut or fill depth to a selected surface. Can also be used to adjust a surface model to match grade at project limits or at other locations e.g. at bridge decks / abutments etc

Provides the ability to offset an entire surface or an area of a surface within a clipping boundary to create a new surface model. This is a quick and easy tool to create e.g. Topsoil Strip surfaces from an Existing Ground surface model.
Surface models provided by Engineers for Existing Ground are often derived from point clouds. The imported TINs often cover large areas and have extremely dense triangulation. For modeling purposes the imported TIN and CAD points derived from the TIN are inefficient in TBC. This command provides the ability to convert the TIN back into a point cloud so that it can be more easily and faster handled in TBC. It can also be reduced in size and point density for faster volume computations.

Computes a surcharge / overexcavation surface by adding a % of cut or fill depth to a selected surface. Can also be used to adjust a surface model to match grade at project limits or at other locations e.g. at bridge decks / abutments etc

Create a new 3D line at an offset and elevation difference to a selected pair of lines where the elevation of the new line is computed by extending the slope defined by the selected pair of lines and applying the elevation difference required. This tool is great for extending pavement or subgrade surfaces where the pavement surface is defined by imported 3D string (lines) data.

Provides the ability to offset an entire surface or an area of a surface within a clipping boundary to create a new surface model. This is a quick and easy tool to create e.g. Topsoil Strip surfaces from an Existing Ground surface model.

This command provides the ability to compute 3D lines at the intersection of two slopes defined by two pairs of lines, with or without vertical or perpendicular offsets. The command is ideal for the computations of subgrade and topsoil adjusted embankment surfaces. All necessary offset lines are computed to facilitate rapid creation of the adjusted surface model.

Surface models provided by Engineers for Existing Ground are often derived from point clouds. The imported TINs often cover large areas and have extremely dense triangulation. For modeling purposes the imported TIN and CAD points derived from the TIN are inefficient in TBC. This command provides the ability to convert the TIN back into a point cloud so that it can be more easily and faster handled in TBC. It can also be reduced in size and point density for faster volume computations.

Create a new 3D line at an offset and elevation difference to a selected pair of lines where the elevation of the new line is computed by extending the slope defined by the selected pair of lines and applying the elevation difference required. This tool is great for extending pavement or subgrade surfaces where the pavement surface is defined by imported 3D string (lines) data.
This command creates text that automatically increments between each text placement e.g. for labeling pads, parking bays or for adding station labels to PDF cross sections that have no text to use for section conversion.

This command allows you to pick an alignment and a selection of linework e.g. for road pavement section lines in order to create the edge lines (pavement edge lines) in the direction of increasing station and / or a boundary around the selected lines. Part of the CAD / PDF cross sections takeoff workflow, this facilitates rapid 3D modeling from converted PDF or CAD cross sections.

Creates points through input of station and offset values with respect to a selected alignment. Elevations can be entered using Elevation, Delta Elevation or Cross Slope from the selected alignment.

Converts selected linework into AOIs for Takeoff reports (Areas of Interest).

This command creates a legend of site improvements applied to surfaces within the project either for takeoff or data modeling purposes. The legend shows the color of the site improvement and the material layer stack and defined material thicknesses for each site improvement used. This automates the creation of drawings for submittals or for use by site personnel to understand a project.

Provides a fast and easy way to determine the surface and plan areas of bounded areas on surface models. The surface areas can be defined by collections of 3D breaklines in the surface with the "Sharp and Texture" property, or areas of the surface where surface textures have been defined. The computed areas can be labeled on the drawing using this command.
This command creates text that automatically increments between each text placement e.g. for labeling pads, parking bays or for adding station labels to PDF cross sections that have no text to use for section conversion.

This command allows you to pick an alignment and a selection of linework e.g. for road pavement section lines in order to create the edge lines (pavement edge lines) in the direction of increasing station and / or a boundary around the selected lines. Part of the CAD / PDF cross sections takeoff workflow, this facilitates rapid 3D modeling from converted PDF or CAD cross sections.

One click access to Getting Started instructions for the RPS Command library

One click access to the Rockpile Solutions website

One click access to the MyRockpile Community forum
One click access to the MyRockpile Library for all your training needs

Upcoming training opportunities with Rockpile Solutions

One click access to the Rockpile Solutions LinkedIn page

One click access to the Rockpile Solutions YouTube page

One click access to the Rockpile Solutions Instagram page

One click access to generate a Support Ticket for RPS staff assistance

The Contact Us command allows you to raise a question to Rockpile Solutions staff directly from inside Trimble Business Center.

Track and manage the installation and update of registered RPS commands
Manage your global RPS command settings

Show the direction of a selected line
Toggle between light and dark Mode menu color schemes
Access to Rockpile Solutions Online Help System.
Creates and manages TBC keyboard shortcuts for commands and provides the ability to save different shortcut definitions into settings files for easy recall.

Utility that provides the ability to save out your custom toolbars and import them back into a different menu configuration

Provides the ability to use voice input to execute any TBC command. This improves productivity and allows the commands to execute as well as the command dialog to be navigated without mouse movement.

Point clouds can be used to create surface models. The resulting surfaces can be large and are hard to report for QA / QC purposes. This command converts a TIN surface, optionally clipped to a boundary into a grid of points based on a regular or alignment based grid, and computes cut / fill values to a reference surface with applied high and low tolerances for reporting purposes.

Copies a layer group and all the layers (that have members) into a new layer group where the group and each layer is named using the existing name with an added prefix or suffix.
RPS Layer Manager provides a rapid way to assign selected layers to layer groups and to add prefix or suffix text to layer names and layer groups. You can also use Search and Replace to modify the names of selected layers.

Copies a layer group and all the layers (that have members) into a new layer group where the group and each layer is named using the existing name with an added prefix or suffix.

A simple editing tool to add additional segments into an existing linestring. Simply click where you require additional nodes and the linestring selected updates by adding additional segments into the existing linestring. You can use this command to insert segments into the line or to add segments at either end of the line.

RPS Layer Manager provides a rapid way to assign selected layers to layer groups and to add prefix or suffix text to layer names and layer groups. You can also use Search and Replace to modify the names of selected layers.

Provides the ability to create two separate plan views displaying different information and synchronize pan and zoom activities so that the same location can be seen in both windows for direct comparison. Combine View Filters, Selection Sets and Lock Views to rapidly identify changes in project revision drawings or to compare weekly / monthly check surveys.

A copy command that provides the ability to multi copy selected objects into a 3D array. User can define the origin, orientation / skew angle, inclination and spacing of the three grid axes. The command is great for creating parking bay striping, site mass haul grids, building piers, stairways and other repetitive patterns on a regular 2D or 3D grid

Create 3D linestrings quickly without the complexity of the Linestring Editor.

Provides the ability to manage plan view rotation in relation to lines and alignments or text items or simply freeform. You can also use this command to reset your plan rotation to North Up. Rotate your plan view as you browse along lines or alignments to make PDF plans or text display items easily readable or simply to maximize the use of screen real estate.

Switch text properties between two selected text objects. Text properties include height, width, text, rotation, oblique angle, justification, aspect ratio, layer, color etc.

Names polygonal line objects using text data located inside the polygon. Used to name lots, pads, parking stalls, buildings and other polygonal objects. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.

A simple editing tool to add additional segments into an existing linestring. Simply click where you require additional nodes and the linestring selected updates by adding additional segments into the existing linestring. You can use this command to insert segments into the line or to add segments at either end of the line.

A copy command that provides the ability to multi copy selected objects into a 3D array. User can define the origin, orientation / skew angle, inclination and spacing of the three grid axes. The command is great for creating parking bay striping, site mass haul grids, building piers, stairways and other repetitive patterns on a regular 2D or 3D grid

Create 3D linestrings quickly without the complexity of the Linestring Editor.

Provides the ability to create two separate plan views displaying different information and synchronize pan and zoom activities so that the same location can be seen in both windows for direct comparison. Combine View Filters, Selection Sets and Lock Views to rapidly identify changes in project revision drawings or to compare weekly / monthly check surveys.

Provides the ability to manage plan view rotation in relation to lines and alignments or text items or simply freeform. You can also use this command to reset your plan rotation to North Up. Rotate your plan view as you browse along lines or alignments to make PDF plans or text display items easily readable or simply to maximize the use of screen real estate.

Converts selected CAD text objects to multiline text objects. Multiline text objects are smarter and have more flexibility in TBC than simple text objects.

Specify color, layer, position tolerance and text case parameters to identify duplicate text items and relayer or delete those identified as duplicates from imported CAD or vector PDF files.

Converts selected CAD text objects to multiline text objects. Multiline text objects are smarter and have more flexibility in TBC than simple text objects.

Specify color, layer, position tolerance and text case parameters to identify duplicate text items and relayer or delete those identified as duplicates from imported CAD or vector PDF files.

Provides the ability to filter a selection of objects in relation to a selected reference line or alignment. User can define parallel or perpendicular or up to a specified skew angle to rapidly find linear features or cross section lines across surfaces. Useful tool with Explode Surface or Explode IFC Shell commands.

Converts selected linework into AOIs for Takeoff reports (Areas of Interest).

Creates a line along the zero cut/fill line between two selected surface models. The lines created are set to sharp and texture boundary and can be optionally included in either or both of the source surface models.

Surface models provided by Engineers for Existing Ground are often derived from point clouds. The imported TINs often cover large areas and have extremely dense triangulation. For modeling purposes the imported TIN and CAD points derived from the TIN are inefficient in TBC. This command provides the ability to convert the TIN back into a point cloud so that it can be more easily and faster handled in TBC. It can also be reduced in size and point density for faster volume computations.

Creates a line along the zero cut/fill line between two selected surface models. The lines created are set to sharp and texture boundary and can be optionally included in either or both of the source surface models.

Surface models provided by Engineers for Existing Ground are often derived from point clouds. The imported TINs often cover large areas and have extremely dense triangulation. For modeling purposes the imported TIN and CAD points derived from the TIN are inefficient in TBC. This command provides the ability to convert the TIN back into a point cloud so that it can be more easily and faster handled in TBC. It can also be reduced in size and point density for faster volume computations.

Converts selected linework into AOIs for Takeoff reports (Areas of Interest).

Creates additional Cut Fill Labels on a cut fill map in user defined spot locations or along linear features defined in the project.

Exports an Alignment to the csv file format required by HCSS Plans.

Create and manage boundaries, boundary collections and boundary groups. Compute and store volume calculations for later recall. Label and annotate drawings with volume labels and tables and generate volume reports for a variety of volumetric scenarios e.g. Stockpiles, Progress, Cut / Fill, Pay Quantities etc.

Reports the plan and slope areas for cut and fill broken down by specified slope ranges on each of two surfaces. The report uses the isopach computed between the two surfaces (e.g. Existing and Subgrade Adjusted Finished Grade) to determine cut and fill areas and then sums the areas of triangles of both surfaces that fall within the defined slope ranges within the computed cut and fill areas. Ideal for the determination of surface finishing / trim areas in fill scenarios.

RPS Layer Manager provides a rapid way to assign selected layers to layer groups and to add prefix or suffix text to layer names and layer groups. You can also use Search and Replace to modify the names of selected layers.

Utilizes the RPS New Layer control to create a new layer, new layer group and assign layer properties including the takeoff categorization, potential site improvement or surface boundaries and associated site improvement attributes.

The RPS Relayer command provides increased productivity when relayering CAD objects to a number of different layers. The user can establish any number of target layers and then simply select the objects to relayer, tag the layer that they want to move them to and OK to execute. The fact that you can relayer to multiple layers quickly and easily can take significant time out of data prep processes.

RPS Layer Manager provides a rapid way to assign selected layers to layer groups and to add prefix or suffix text to layer names and layer groups. You can also use Search and Replace to modify the names of selected layers.

Provides the ability to create two separate plan views displaying different information and synchronize pan and zoom activities so that the same location can be seen in both windows for direct comparison. Combine View Filters, Selection Sets and Lock Views to rapidly identify changes in project revision drawings or to compare weekly / monthly check surveys.

A copy command that provides the ability to multi copy selected objects into a 3D array. User can define the origin, orientation / skew angle, inclination and spacing of the three grid axes. The command is great for creating parking bay striping, site mass haul grids, building piers, stairways and other repetitive patterns on a regular 2D or 3D grid

Utilizes the RPS New Layer control to create a new layer, new layer group and assign layer properties including the takeoff categorization, potential site improvement or surface boundaries and associated site improvement attributes.

The RPS Relayer command provides increased productivity when relayering CAD objects to a number of different layers. The user can establish any number of target layers and then simply select the objects to relayer, tag the layer that they want to move them to and OK to execute. The fact that you can relayer to multiple layers quickly and easily can take significant time out of data prep processes.

Provides the ability to manage plan view rotation in relation to lines and alignments or text items or simply freeform. You can also use this command to reset your plan rotation to North Up. Rotate your plan view as you browse along lines or alignments to make PDF plans or text display items easily readable or simply to maximize the use of screen real estate.

Create multiple copies of any objects quickly on the same or different layers, in 2D or 3D and in any view

Provides manual and fully automated methods to join CAD or PDF vector lines together quickly and easily. Solves common problems like line gaps, overlaps, crossovers, lateral gaps, lines on different layers, lines with different names or colors to provide an extremely fast way to join lines. Line segments can be selected in the most convenient location not just at the ends that you wish to join.

Provides the ability to crop selected lines either side of a selected line or to remove the segments of selected lines between a pair of lines. This is useful to remove e.g. Contour lines from pavement areas or around curb and gutter sections, where more precise modeling techniques are being used.

Name by Layer - Names line objects using the name of the objects layer. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.
Layer by Name - Relayers objects based on the objects name. Layered objects can be placed in Layer Groups using a Layer Group mapping using filter elements of the objects name. This is useful for organizing surveyed data e.g. for utility relocates

Names polygonal line objects using text data located inside the polygon. Used to name lots, pads, parking stalls, buildings and other polygonal objects. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.

Reverse the direction of selected linestrings, CAD lines or polylines using a simple switch direction, align to an alignment or reference line, clockwise / anticlockwise (closed lines), or align with slope (from first to last node of the selected lines).

Creates 2D and 3D linestrings with a range of controls to manage elevation input and formulaic adjustment including 2D, single height, multiheight, multiheight auto and multiheight from surface. Also includes ability to create lines with a preset number of nodes, can autoclose and provide grip editing while in the command. Can also create curve elements and VPI only nodes also. Ideal for takeoff digitizing of linework or for data prep purposes.

A copy command that provides the ability to multi copy selected objects into a 3D array. User can define the origin, orientation / skew angle, inclination and spacing of the three grid axes. The command is great for creating parking bay striping, site mass haul grids, building piers, stairways and other repetitive patterns on a regular 2D or 3D grid

Provides manual and fully automated methods to join CAD or PDF vector lines together quickly and easily. Solves common problems like line gaps, overlaps, crossovers, lateral gaps, lines on different layers, lines with different names or colors to provide an extremely fast way to join lines. Line segments can be selected in the most convenient location not just at the ends that you wish to join.

Provides the ability to crop selected lines either side of a selected line or to remove the segments of selected lines between a pair of lines. This is useful to remove e.g. Contour lines from pavement areas or around curb and gutter sections, where more precise modeling techniques are being used.

Provides the ability to create two separate plan views displaying different information and synchronize pan and zoom activities so that the same location can be seen in both windows for direct comparison. Combine View Filters, Selection Sets and Lock Views to rapidly identify changes in project revision drawings or to compare weekly / monthly check surveys.

Provides the ability to manage plan view rotation in relation to lines and alignments or text items or simply freeform. You can also use this command to reset your plan rotation to North Up. Rotate your plan view as you browse along lines or alignments to make PDF plans or text display items easily readable or simply to maximize the use of screen real estate.

Provides a work process tool to cleanup and sort imported CAD files. The command includes a CAD Block processor to manage and explode imported blocks, a Layer control to manage and group imported layers based on predefined rulesets, and a set of miscellaneous controls to delete imported plan sets, delete AEC object references, zero length lines and empty unprotected layers, change text to multiline text and change text styles to stroke fonts for improved graphics speed.

Converts selected CAD text objects to multiline text objects. Multiline text objects are smarter and have more flexibility in TBC than simple text objects.

Imported Solids, 3DShell or mesh objects from IFC, DWG and DGN files can be exploded into component lines and points using this command. The command handles solids by breaking them into top, bottom and side objects or 3D polygons on separate layers so that the data can be used as source data for surface models. 3D linear features can be re-created through use of the Filter by Alignment command.

Specify color, layer, position tolerance and text case parameters to identify duplicate text items and relayer or delete those identified as duplicates from imported CAD or vector PDF files.

Converts selected CAD text objects to multiline text objects. Multiline text objects are smarter and have more flexibility in TBC than simple text objects.

Imported Solids, 3DShell or mesh objects from IFC, DWG and DGN files can be exploded into component lines and points using this command. The command handles solids by breaking them into top, bottom and side objects or 3D polygons on separate layers so that the data can be used as source data for surface models. 3D linear features can be re-created through use of the Filter by Alignment command.

Specify color, layer, position tolerance and text case parameters to identify duplicate text items and relayer or delete those identified as duplicates from imported CAD or vector PDF files.

Name by Layer - Names line objects using the name of the objects layer. This is a useful tool to prepare imported CAD data for field users of Trimble Siteworks or SCS900 etc.
Layer by Name - Relayers objects based on the objects name. Layered objects can be placed in Layer Groups using a Layer Group mapping using filter elements of the objects name. This is useful for organizing surveyed data e.g. for utility relocates

Reverse the direction of selected linestrings, CAD lines or polylines using a simple switch direction, align to an alignment or reference line, clockwise / anticlockwise (closed lines), or align with slope (from first to last node of the selected lines).

Provides a quick and easy way to null out or modify VPIs on selected sections of 3D linestrings, adjust and prorate elevations for bridge beam deflections or to taper linework over selected distances to match existing grade. You can use this command in Spot mode to elevate lines. Plane Mode allows you to elevate e.g. curb lines onto tilted planes defined by 3 points. Surface Mode allows you to elevate e.g. curb lines onto a grading framework surface e.g. for Parking Lots. In Plane and Surface Mode you can specifically define how points are created around curve sections to improve the quality and consistency of your models.

Combines multiple TIN surfaces from a design into a single TIN surface model comprising multiple islands. For example where an over excavation surface on a corridor model comes and goes along the alignment, or where the left embankment and right embankment were designed as separate components and you want to combine them into a single surface for TBC corridor or machine control purposes.

Explodes a selected TIN surface model into 3D lines and or points. The explode process eliminates duplicate lines. The exploded surface can then be edited to remove erroneous data e.g. erroneous triangle sides or to be combined with other data to create a new surface model. Explode process also provides advanced filter controls to facilitate breakline, drapeline and boundary identification and extraction.

Creates a line along the zero cut/fill line between two selected surface models. The lines created are set to sharp and texture boundary and can be optionally included in either or both of the source surface models.

Combines multiple TIN surfaces from a design into a single TIN surface model comprising multiple islands. For example where an over excavation surface on a corridor model comes and goes along the alignment, or where the left embankment and right embankment were designed as separate components and you want to combine them into a single surface for TBC corridor or machine control purposes.

Explodes a selected TIN surface model into 3D lines and or points. The explode process eliminates duplicate lines. The exploded surface can then be edited to remove erroneous data e.g. erroneous triangle sides or to be combined with other data to create a new surface model. Explode process also provides advanced filter controls to facilitate breakline, drapeline and boundary identification and extraction.

Template driven command that creates multiple offset lines (fully curvilinear lines) for multiple surfaces (finished grade and subgrade) on multiple layers (one per feature line) from selected source lines defined using offset and elevation, offset and delta elevation, offset and slope definitions. Ideal for curb & gutter, barriers, gabion walls, site /subdivision roads and more.

Provides the ability to create points and or lines using station and combination of either Offset and Elevation, Offset and Delta Elevation, Offset and Slope, Slope and Elevation, Slope and Delta Elevation or Slope and Target Surface. This provides an effective means of defining sideslopes, benches, berms, ponds or pad areas etc.

Creates a line along the zero cut/fill line between two selected surface models. The lines created are set to sharp and texture boundary and can be optionally included in either or both of the source surface models.

Template driven command that creates multiple offset lines (fully curvilinear lines) for multiple surfaces (finished grade and subgrade) on multiple layers (one per feature line) from selected source lines defined using offset and elevation, offset and delta elevation, offset and slope definitions. Ideal for curb & gutter, barriers, gabion walls, site /subdivision roads and more.

Provides the ability to create points and or lines using station and combination of either Offset and Elevation, Offset and Delta Elevation, Offset and Slope, Slope and Elevation, Slope and Delta Elevation or Slope and Target Surface. This provides an effective means of defining sideslopes, benches, berms, ponds or pad areas etc.

This powerful tool provides geometric selection properties for imported CAD or PDF linework. Initially conceived for the cross section takeoff workflows, this tool provides geometric controls that can be combined for extremely rapid selection and relayering of objects using length, aspect ratio and node count.

This command provides two main abilities, Nudge Line and Nudge Node. Nudge Line moves a selected line laterally by a defined amount in order to fix a surface model where two lines that define the top and bottom of a vertical wall or face lie on top of each other but separated vertically. Nudge Node is for cross sections where two or more nodes in the cross section lie in the same XY location but are separated vertically.

Converts chorded linework into optimized curvilinear linestrings in both horizontal and vertical components for use in stringless paving and to improve 3D models for corridors. Can also be used to convert chorded PDF Vector lines into curvilinear lines for modeling purposes.

Imports boring log data from a CSV file to create site (Takeoff) boring logs in order to rapidly build strata layers for earthworks quantity purposes.

Extracts vectors from georeferenced PDF images on demand using automatic and manual process controls. Lines can be layered, joined and elevated in the process, eliminating multiple Takeoff steps and increasing productivity.

Creates 2D and 3D linestrings with a range of controls to manage elevation input and formulaic adjustment including 2D, single height, multiheight, multiheight auto and multiheight from surface. Also includes ability to create lines with a preset number of nodes, can autoclose and provide grip editing while in the command. Can also create curve elements and VPI only nodes also. Ideal for takeoff digitizing of linework or for data prep purposes.

This powerful tool provides geometric selection properties for imported CAD or PDF linework. Initially conceived for the cross section takeoff workflows, this tool provides geometric controls that can be combined for extremely rapid selection and relayering of objects using length, aspect ratio and node count.

This command provides two main abilities, Nudge Line and Nudge Node. Nudge Line moves a selected line laterally by a defined amount in order to fix a surface model where two lines that define the top and bottom of a vertical wall or face lie on top of each other but separated vertically. Nudge Node is for cross sections where two or more nodes in the cross section lie in the same XY location but are separated vertically.

Converts chorded linework into optimized curvilinear linestrings in both horizontal and vertical components for use in stringless paving and to improve 3D models for corridors. Can also be used to convert chorded PDF Vector lines into curvilinear lines for modeling purposes.

Creates additional Cut Fill Labels on a cut fill map in user defined spot locations or along linear features defined in the project.

Copy data from one project to another or within an existing project using our virtual VCL file via the Windows clipboard. Ideal for creating copies of sheet sets complete with all settings within a project or for transferring information from one project into another without having to use Export and Import processes.

Paste information from the Windows clipboard directly into your project drawings. Use with your favorite Windows clipping tool (Snagit, Snip and Paste etc.) to capture PDF sheet details, excel spreadsheet tables, images, text or virtual VCL data generated using RPS Copy to Clipboard command.

Exports an Alignment to the csv file format required by HCSS Plans.
We would love to show you how our tools can help you increase your productivity.
Fill out the form to schedule a demo or call us at (720) 797-8001 today!